apnscp supports simple MySQL database snapshots as of August 28, 2016. Snapshots are ideal for preserving your database structure before a software update or any situation in which there is risk of loss of data not covered by the nightly backups. Snapshots perform a full database export and stores this file, uncompressed, in your backup directory. Snapshots are automatically removed after 5 days. Snapshots that have been taken may be used, along with automated backups, for rollbacks within the control panel.
Using snapshots
Snapshots are created within the control panel:
- Visit Databases > MySQL Manager > List Users and Databases
- Select the database to snapshot.
- Select Snapshot from the actions available in the dropdown.
- A snapshot will process, which may take a few minutes depending upon size. Once completed a modal dialog will pop-in confirming success.
Snapshots may be accessed within the control panel for 5 days after which time they are automatically deleted. A better long-term solution is to use Databases > MySQL Backups within the control panel to configure automatic backups with rollout.
Snapshots are never compressed, located within your home directory, under mysql_backups/, and follow the format DBNAME–YYYYMMDDHHMMSS-snapshot.sql
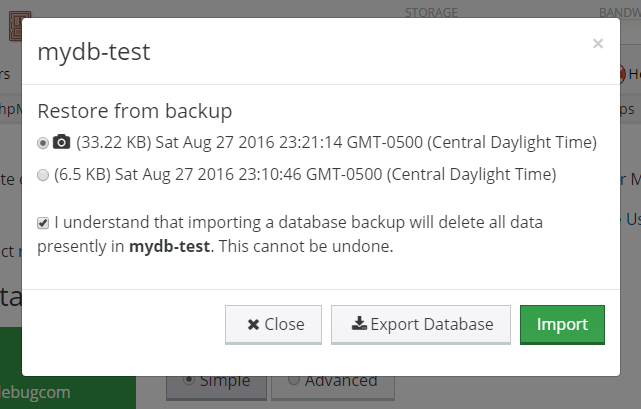
Restoring from a snapshot or backup
Restoration from a snapshot (short-term) or backup (long-term) can be done easily within the control panel:
- Visit Databases > MySQL Manager > List Users and Databases
- Select the database to restore.
- Select Restore from Backup from the actions available in the dropdown.
- Choose which backup to restore from.
- Backups are sorted by most recent first. Snapshots are denoted by a camera icon.
- Check the box to confirm deletion of your current database.
- All data in the database will be emptied. All backup tasks and user privileges will be preserved.
- Select Import
Using non-CP exports as restore points
To use a user-created backup to restore from, such as an older snapshot no longer present in mysql_backups/ or even a phpMyAdmin export, upload the file to mysql_backups/ within your home directory via FTP or the control panel (Files > File Manager). The backup must follow a few rules:
- File name must be named DBNAME-20 followed by exactly 6 digits (YYMMDD)
- Or optionally followed by 1 or more digits and “-snapshot”
- End in one of the supported formats: .sql, .zip, .tar, .gz
Once detected successfully, the backup will appear as an option to restore from.